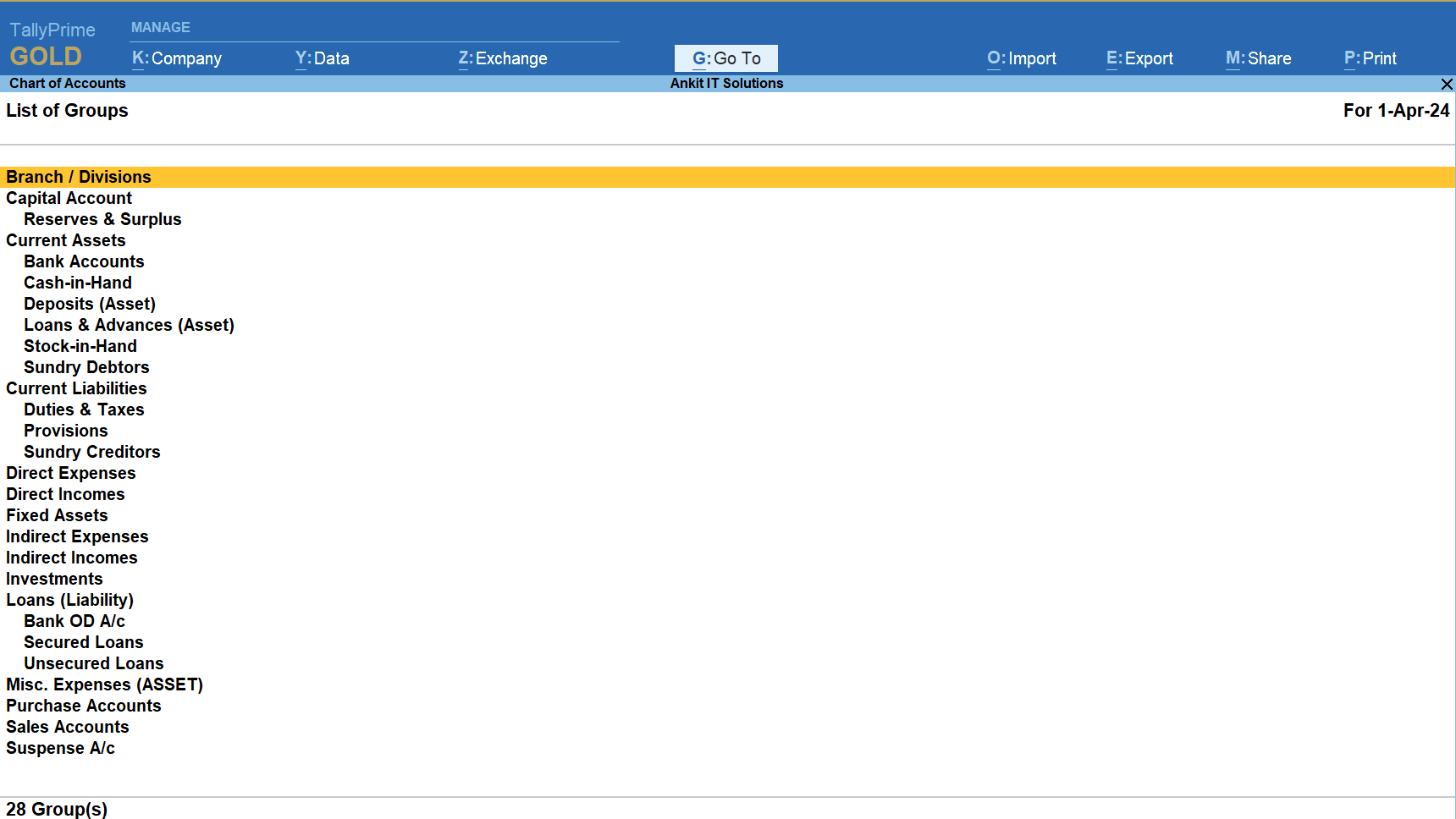
When you create a company in TallyPrime, it automatically comes with 28 predefined groups. These groups help you organize all your accounting data like ledgers, stock items, and transactions in a structured way.
Understanding these groups is very important for beginners, accountants, and business owners using Tally for financial management.
What is a Group in Tally?
In TallyPrime, a Group is used to classify ledgers into categories. This helps you:
- Easily create reports like Balance Sheet, Profit & Loss A/c, etc.
- Maintain proper accounting structure.
- Apply correct GST or inventory settings.
Types of Groups in Tally
Tally groups are divided into two types:
- Primary Groups – Main heads like Assets, Liabilities, Income, and Expenses.
- Sub-Groups – Predefined sub-categories under each primary group.
Out of the 28 predefined groups, 15 are primary and 13 are sub-groups.
List of 28 Predefined Groups in TallyPrime
Here is the complete list, grouped under their category with examples:
🔴 Capital & Liabilities
- Capital Account – Owner’s capital, reserve fund.
- Loans (Liability) – Secured/Unsecured loans taken.
- Current Liabilities – Outstanding expenses, dues, etc.
- Sundry Creditors – People/businesses you owe money to.
- Reserves & Surplus – Accumulated profits or reserves.
🟠 Assets
- Fixed Assets – Furniture, computer, building.
- Investments – FD, mutual funds, shares.
- Current Assets – Assets expected to be used within a year.
- Sundry Debtors – Customers who owe you money.
- Cash-in-Hand – Cash balance, like Petty Cash.
- Bank Accounts – SBI, HDFC, ICICI, etc.
- Bank OD A/c – Bank overdraft accounts.
- Deposits (Assets) – Security deposit, rent deposit.
- Loans & Advances (Assets) – Advance paid to staff, others.
🟢 Income
- Sales Account – All types of sales (cash/credit).
- Direct Incomes – Freight received, commission earned.
- Indirect Incomes – Interest received, discount earned.
🔵 Expenses
- Purchase Account – All types of purchases.
- Direct Expenses – Freight paid, wages (factory).
- Indirect Expenses – Salary, rent, stationery.
⚙️ Inventory Related
- Stock-in-Hand – Closing stock.
- Duties & Taxes – GST, VAT, TDS, etc.
- Provisions – Provision for tax, bad debts.
- Misc. Expenses (Assets) – Preliminary expenses.
🧾 Sales & Purchase Classification
- Branch/Divisions – For multiple locations.
- Suspense A/c – Temporary unclassified entries.
- Profit & Loss A/c – Auto-generated from income & expenses.
- Advance Income – Income received in advance.
Method 1 for see the 28 predefined groups of tallyprime
Step 1- Click on Alter
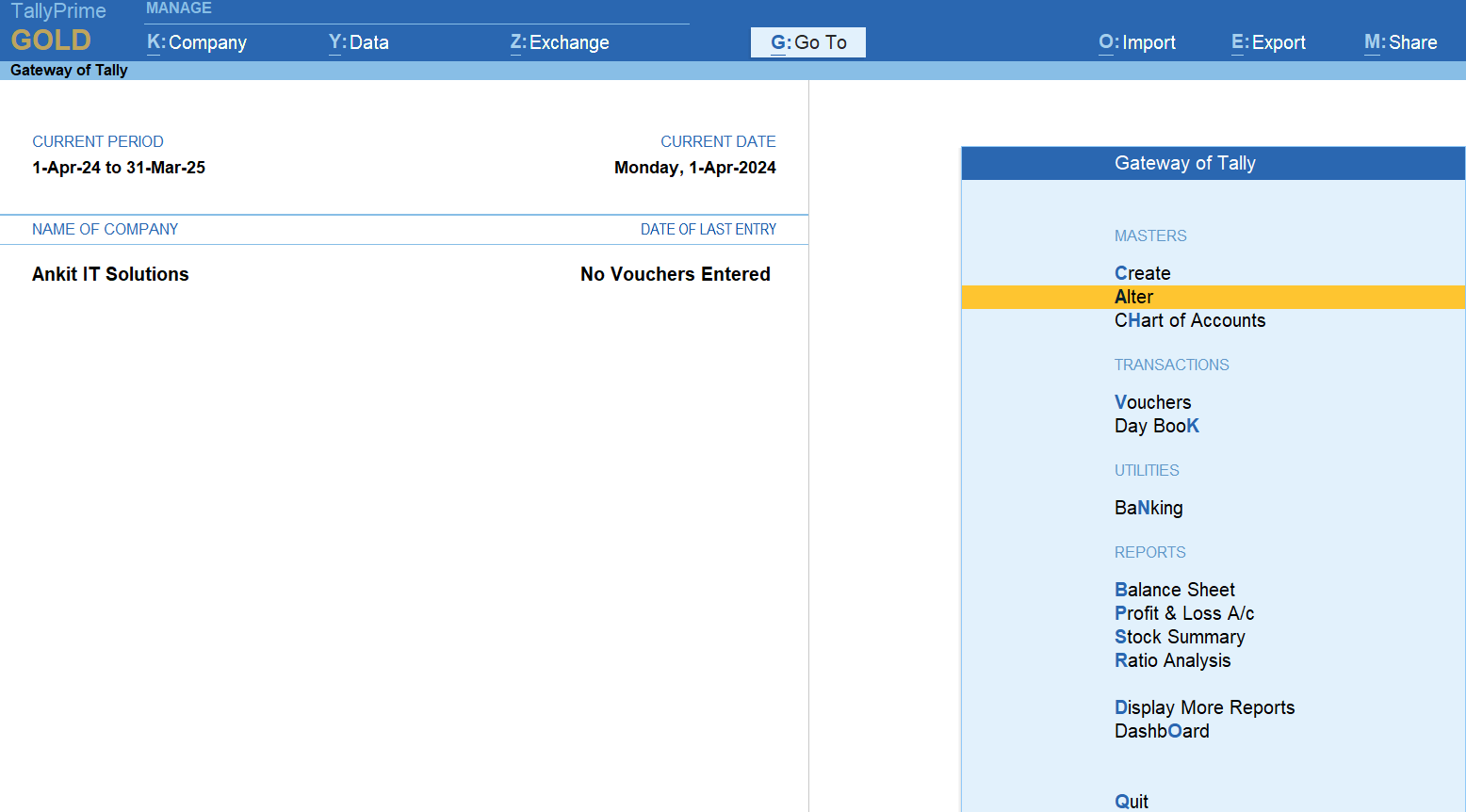
Step 2- Click on Group
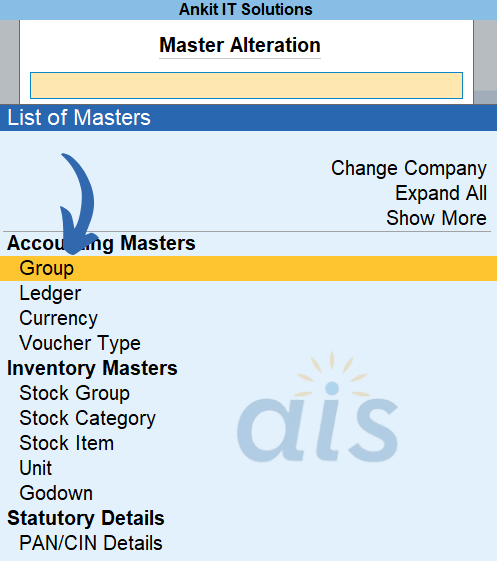
after it here are 28 predefined groups in Tallyprime you can see
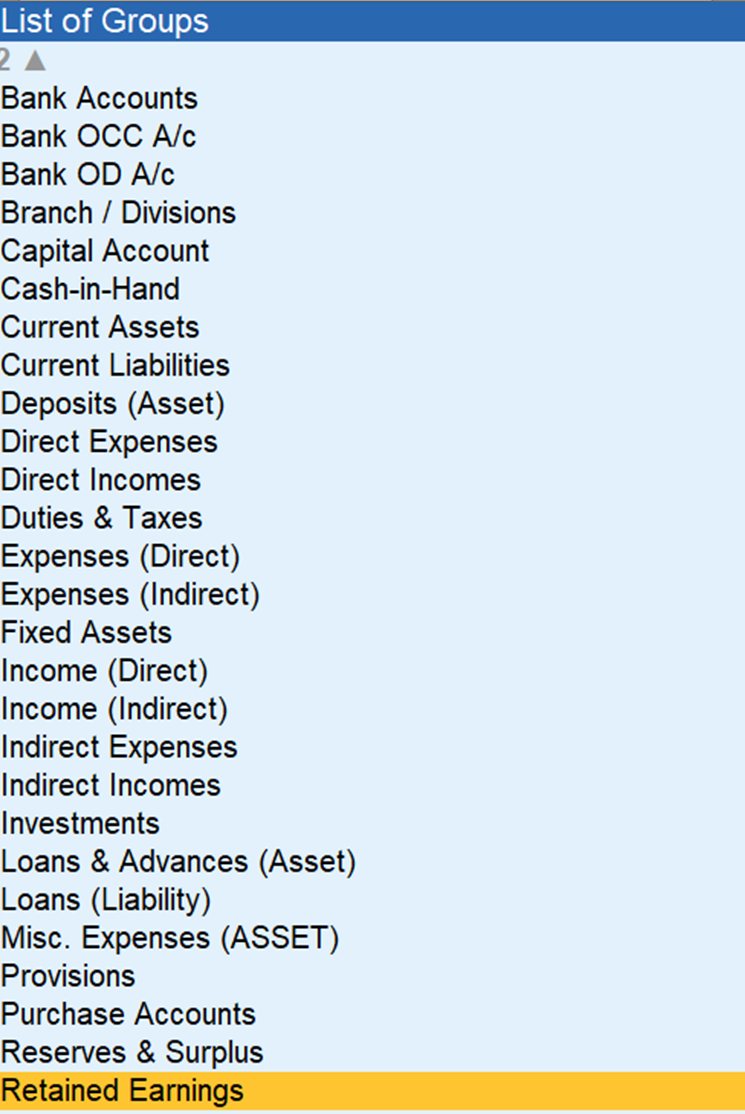
Let’s explore each group with definition and 5 real-life examples for better understanding.
1. Bank Accounts
Bank ledgers contain relevant information about banks used to make or receive payments.
Examples:
- HDFC Bank A/c
- State Bank of India A/c
- Axis Bank A/c
- ICICI Bank A/c
- Canara Bank A/c
2. Bank OCC A/c (Open Cash Credit)
Used by small or medium enterprises to manage working capital through overdraft against security.
Examples:
- HDFC OCC A/c
- SBI OCC A/c
- Punjab National Bank OCC A/c
- Axis OCC A/c
- Bank of Baroda OCC A/c
3. Bank OD A/c (Overdraft Account)
When a business is allowed to withdraw more than its bank balance.
Examples:
- SBI OD A/c
- ICICI OD A/c
- HDFC OD A/c
- Axis Bank OD A/c
- PNB OD A/c
4. Branch / Divisions
Used to record transactions of different business locations or departments.
Examples:
- Mumbai Branch
- Delhi Office
- Online Division
- Retail Store – Surat
- South Zone Division
5. Capital Account
Indicates the owner’s or partner’s investment in the business.
Examples:
- Ankit Capital
- Partner A Capital
- Opening Capital
- Capital Contribution
- Owner’s Equity
6. Cash-in-Hand
Cash available physically with the business.
Examples:
- Cash
- Petty Cash
- Office Cash
- Sales Collection Cash
- Cash Counter A/c
7. Current Assets
Assets that can be converted into cash within one year.
Examples:
- Sundry Debtors
- Bills Receivable
- Short-Term Investments
- Advance to Staff
- Prepaid Rent
8. Current Liabilities
Liabilities payable within one year.
Examples:
- Sundry Creditors
- Outstanding Salary
- GST Payable
- Advance Received from Customers
- TDS Payable
9. Deposits (Asset)
Fixed or security deposits made by the company.
Examples:
- Security Deposit with Landlord
- Rent Deposit
- Telephone Deposit
- Electricity Deposit
- FD with ICICI Bank
10. Direct Expenses
Expenses directly related to the production or trading activity.
Examples:
- Wages
- Freight Inward
- Power & Fuel
- Carriage Inward
- Packing Charges
11. Direct Incomes
Income from core business activities.
Examples:
- Freight Income
- Commission Received
- Transportation Charges Income
- Service Income
- Consultation Fees
12. Duties & Taxes
Contains all tax-related ledgers.
Examples:
- CGST Payable
- SGST Payable
- IGST Payable
- TDS Payable
- VAT Payable
13. Expenses (Direct)
Same as Direct Expenses – directly linked to production or purchase.
Examples:
- Factory Rent
- Raw Material Cost
- Loading Charges
- Manufacturing Expenses
- Direct Labour
14. Fixed Assets
Long-term assets used in business operations.
Examples:
- Furniture & Fixtures
- Computers
- Office Equipment
- Building
- Vehicles
15. Income (Direct)
(Repeats same as Direct Income) – Main source of revenue.
Examples:
- Sales Income
- Export Service Income
- Project Charges Income
- Freight Service Income
- Product Design Income
16. Income (Indirect)
Earnings not directly from core business.
Examples:
- Interest Received
- Dividend Income
- Rent Received
- Discount Received
- Scrap Sales
17. Indirect Incomes
Same as above, not related to main business.
Examples:
- Sale of Old Furniture
- Sale of Waste Material
- Interest on Bank FD
- Cash Discount Received
- Profit on Asset Sale
18. Investments
Investments made to earn income or for capital gain.
Examples:
- Shares in Tata Steel
- Mutual Funds
- FD in SBI
- Investment in Gold
- Land Purchased for Investment
19. Loans & Advances (Asset)
Loans given or advances for non-trading purposes.
Examples:
- Advance to Staff
- Loan to Partner
- Advance for Machinery Purchase
- Advance Rent Paid
- Loan to Vendor
20. Loans (Liability)
Loans taken by the business.
Examples:
- Loan from SBI
- Vehicle Loan from HDFC
- Machinery Loan from Axis Bank
- Term Loan from ICICI
- Loan from Director
21. Provisions
Expenses payable next year but belong to current year.
Examples:
- Salary Payable (March)
- Bonus Payable
- Leave Encashment Payable
- Audit Fee Payable
- Provision for Tax
22. Purchase Accounts
Used to record business purchases.
Examples:
- Raw Material Purchase
- Finished Goods Purchase
- Local Purchase A/c
- GST Purchase A/c
- Trading Goods Purchase
23. Reserves & Surplus
Accumulated profits or reserved funds.
Examples:
- General Reserve
- Capital Redemption Reserve
- Profit & Loss A/c (Credit Balance)
- Revaluation Reserve
- Retained Earnings
24. Retained Earnings
Cumulative profits not paid out as dividends.
Examples:
- Retained Earnings A/c
- Earnings Reserve
- Unappropriated Profit
- Retained Profit from Previous Year
- Earnings Balance
25. Secured Loans
Loans backed by collateral/security.
Examples:
- Housing Loan
- Gold Loan
- Car Loan (Secured)
- Machinery Loan with Asset Security
- Term Loan with Land Collateral
26. Stock-in-Hand
Closing stock available at the end of the period.
Examples:
- Finished Goods Stock
- Raw Material Stock
- Packing Material Stock
- Trading Goods Stock
- Closing Inventory
27. Sundry Creditors
Vendors to whom the business owes money.
Examples:
- ABC Traders
- XYZ Suppliers
- Ram & Co.
- Raw Material Suppliers
- Software Vendor
28. Sundry Debtors
Customers who owe money to the business.
Examples:
- Ankit Enterprises
- Rahul Distributors
- Shine Traders
- ABC Stores
- Online Customer (Invoice Basis)
29. Suspense A/c
Temporary account to hold unclassified entries.
Examples:
- Suspense – Opening Balance Difference
- Suspense – Unknown Deposit
- Suspense Payment
- Temporary Advance
- Unmatched Entry Account
30. Unsecured Loans
Loans taken without any collateral.
Examples:
- Personal Loan from Friend
- Unsecured Loan from Partner
- Business Loan without Security
- Director’s Loan (Unsecured)
- Loan from NBFC without Collateral